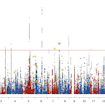
Mark Daly and colleagues report the results of a large genome-wide association meta-analysis of more than 18,000 individuals with ASD, including the newly genotyped Danish iPSYCH cohort.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

Mark Daly and colleagues report the results of a large genome-wide association meta-analysis of more than 18,000 individuals with ASD, including the newly genotyped Danish iPSYCH cohort.

Evan Eichler and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of de novo mutations from individuals with ASD, intellectual disability or developmental delay and found new risk genes for neurodevelopmental disorders.
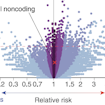
Stephan Sanders and colleagues used a machine learning approach to analyze whole-genome sequencing data from more than 1,900 SSC families and found that de novo noncoding variants in distal regions of promoters confer risk of ASD.
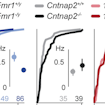
Dan Feldman and colleagues analyzed four mouse models of autism and found that alterations in the excitation-inhibition ratio may serve as a homeostatic mechanism to prevent network hyperexcitability.
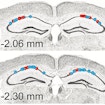
Assessing network and synaptic communication in the hippocampus of behaving Fmr-1 null mice, André Fenton and colleagues showed altered network communication linked to behavioral alterations in fragile X syndrome.
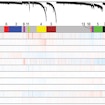
In comparing gene expression profiles and SNP risk across psychiatric disorders, Michael Gandal, Daniel Geschwind and colleagues found that shared genetic risk manifests in alterations in gene networks.
Using a mouse lacking brain-localized NHE9, Edwards shows that pH gradients affect neuronal communication and autism-like behaviors.
By assessing the 16p11.2 deletion autism mouse model, Ted Abel and colleagues uncover male-specific vulnerabilities in striatal signaling and reward function.