IMFAR 2015
Recent articles
Hyperactive fish point to new drug treatments for autism
A drug that mimics estrogen eases hyperactivity in zebrafish lacking the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2. The results highlight the potential of the tiny fish for screening autism treatments.

Hyperactive fish point to new drug treatments for autism
A drug that mimics estrogen eases hyperactivity in zebrafish lacking the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2. The results highlight the potential of the tiny fish for screening autism treatments.
Brain structure abnormalities predict repetitive behaviors
Among babies who go on to receive a diagnosis of autism at age 2, alterations in brain structures forecast the severity of repetitive behaviors. The preliminary results were presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Brain structure abnormalities predict repetitive behaviors
Among babies who go on to receive a diagnosis of autism at age 2, alterations in brain structures forecast the severity of repetitive behaviors. The preliminary results were presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
New approach powers up search for autism genes
A statistical trick can help researchers home in on subtle genetic blips that contribute to autism, according to unpublished results presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

New approach powers up search for autism genes
A statistical trick can help researchers home in on subtle genetic blips that contribute to autism, according to unpublished results presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Takeaways from IMFAR 2015
Scientists and the autism community come together for the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Takeaways from IMFAR 2015
Scientists and the autism community come together for the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Brain structure abnormalities in autism vary by gender
A region of the brain involved in recognizing faces appears to be thinner than usual in women with autism and thicker than usual in men with the disorder. The preliminary results were presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Brain structure abnormalities in autism vary by gender
A region of the brain involved in recognizing faces appears to be thinner than usual in women with autism and thicker than usual in men with the disorder. The preliminary results were presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Primary care doctors unprepared to help adults with autism
Healthcare providers in the U.S. are ill equipped to care for the growing number of adults with autism, according to unpublished results presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Primary care doctors unprepared to help adults with autism
Healthcare providers in the U.S. are ill equipped to care for the growing number of adults with autism, according to unpublished results presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Dispatches from IMFAR 2015
These short reports from our journalists give you the inside scoop on developments at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research.

Dispatches from IMFAR 2015
These short reports from our journalists give you the inside scoop on developments at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research.
Device predicts future word use in toddlers with autism
An automated analysis of the speech-like sounds from 3-year-olds with autism predicts their word use four months later, according to unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Device predicts future word use in toddlers with autism
An automated analysis of the speech-like sounds from 3-year-olds with autism predicts their word use four months later, according to unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Rare regressive disorder is not autism, new findings suggest
Children who are diagnosed with autism after drastically and suddenly losing cognitive abilities may actually have a distinct disorder, according to data presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Rare regressive disorder is not autism, new findings suggest
Children who are diagnosed with autism after drastically and suddenly losing cognitive abilities may actually have a distinct disorder, according to data presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Lopsided brain activity marks motor deficits in autism
Uneven wiring in the brain’s motor circuitry predicts movement difficulties in children with autism, according to unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Lopsided brain activity marks motor deficits in autism
Uneven wiring in the brain’s motor circuitry predicts movement difficulties in children with autism, according to unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Coding error caused layoffs at National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke this week, source says
Thirty employees—including 11 lab heads—at the institute should “immediately return to work,” according to an email the institute’s Office of Human Resources sent to top administration at the institute Wednesday evening.

Coding error caused layoffs at National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke this week, source says
Thirty employees—including 11 lab heads—at the institute should “immediately return to work,” according to an email the institute’s Office of Human Resources sent to top administration at the institute Wednesday evening.
PTEN problems underscore autism connection to excess brain fluid
Damaging variants in the autism-linked gene cause congenital hydrocephalus—a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain—by turbocharging a downstream signaling pathway that promotes the growth of cells, according to a new study.
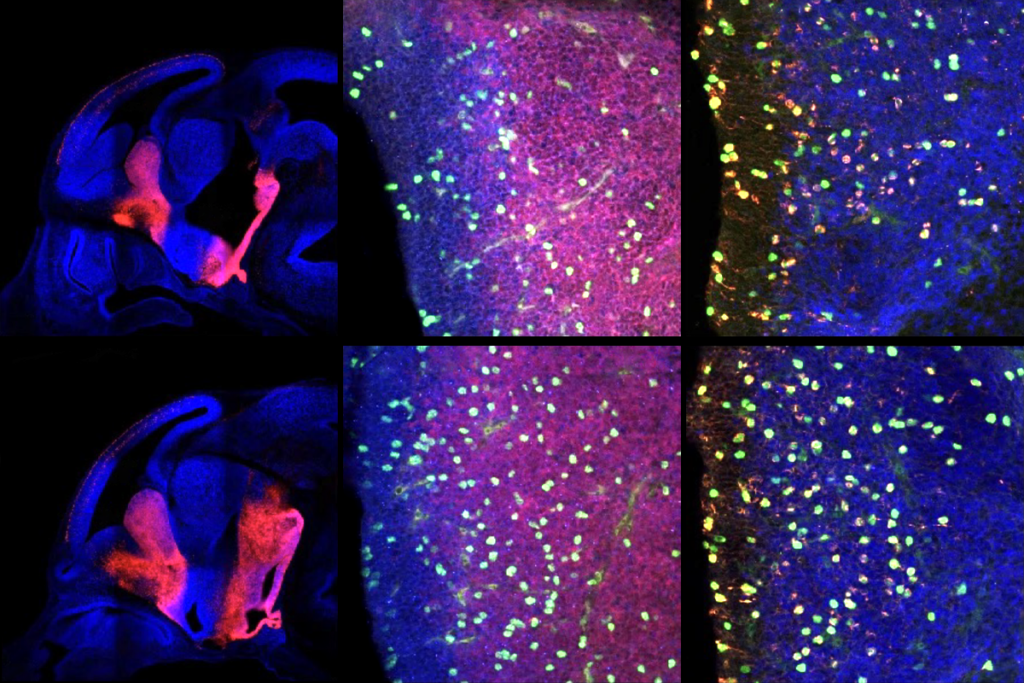
PTEN problems underscore autism connection to excess brain fluid
Damaging variants in the autism-linked gene cause congenital hydrocephalus—a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain—by turbocharging a downstream signaling pathway that promotes the growth of cells, according to a new study.
U.S. health agency purge includes 10 lab heads at National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
The reasons for selecting these researchers—who have led work on neuronal migration, dopamine receptors in neuronal signaling and the structure of ion channels, among other areas—remain unclear.
U.S. health agency purge includes 10 lab heads at National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
The reasons for selecting these researchers—who have led work on neuronal migration, dopamine receptors in neuronal signaling and the structure of ion channels, among other areas—remain unclear.