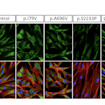
Michael Piper and colleagues confirmed and extended the association of USP9X loss-of-function mutations with a neurodevelopmental syndrome in both sexes, driven by changes in multiple signaling pathways.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

Michael Piper and colleagues confirmed and extended the association of USP9X loss-of-function mutations with a neurodevelopmental syndrome in both sexes, driven by changes in multiple signaling pathways.

Joseph Buxbaum and colleagues in the Autism Sequencing Consortium reported the largest exome sequencing study of ASD to date, identifying 102 risk genes at a false discovery rate of 0.1 or less.
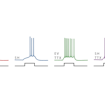
Gina Turrigiano and colleagues showed that loss of Shank3 disrupts homeostatic plasticity and that this deficit can be rescued by the mood-stabilizing drug lithium (Li+).
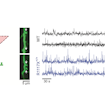
Alex Kwan and colleagues used in vivo calcium imaging to show that a mutation in Shank3 associated with schizophrenia affects the activity of inhibitory neurons in the cortex, ultimately leading to enhanced activity of excitatory neurons and altered behavior in mice.
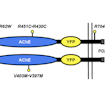
Catharine Rankin, Kurt Haas, Paul Pavlidis and colleagues used machine vision to find that mutations linked to ASD risk genes are associated with changes in habituation of response probability in C. elegans
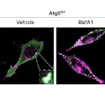
David Sulzer and colleagues used conditional knockout mice of Atg7, a protein involved in autophagy, to study the effects of loss of autophagy on the structure and function of striatal spiny projection neurons, as well as on behaviors relevant to ASD.
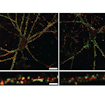
Nael Nadif Kasri and colleagues used micro-electrode array assays to demonstrate common neuronal network phenotypes associated with genes underlying Kleefstra spectrum syndrome.
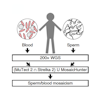
Joseph Gleeson and colleagues used deep whole-genome sequencing and genotyping of sperm DNA to stratify ASD risk in offspring due to de novo mutation.