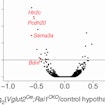
Liqun Luo uses conditional, cell-type-specific RAI1 deletions in mice to assess how loss of RAI1 contributes to neurodevelopmental phenotypes in Smith-Magenis syndrome.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

Liqun Luo uses conditional, cell-type-specific RAI1 deletions in mice to assess how loss of RAI1 contributes to neurodevelopmental phenotypes in Smith-Magenis syndrome.
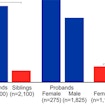
By assessing human accelerated regions (HARs) in healthy individuals and those with ASD, Chris Walsh shows HARs regulate human social and cognitive behavior and ASD risk.
Huda Zoghbi and Stelios Smirnakis investigate how opposing molecular deficits in MeCP2 duplication and Rett syndromes lead to similar behavioral phenotypes.
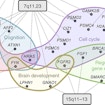
Simons Center for Data Analysis scientist Olga Troyanskaya has developed a machine-learning tool that uses neural interaction networks to predict autism risk genes.
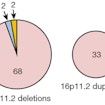
Evan Eichler reconstructs the evolution of chromosome 16p11.2 and finds most disease-causing rearrangements map within a H. sapiens-specific duplication containing BOLA2.
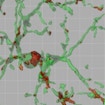
Beth Stevens shows that, in MeCP2 null mice, microglia excessively eliminate presynaptic inputs, targeting synapses previously weakened by MeCP2 loss in other CNS cell types.
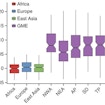
Joseph Gleeson and colleagues have generated a publically accessible whole-exome variome from 1,111 unrelated individuals within the Greater Middle East Variome Consortium.
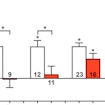
David Ginty shows that four different mice harboring mutations in ASD risk genes have altered peripheral sensory neuron processing that contributes to ASD-like phenotypes.