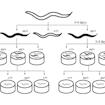
Paul Sternberg and colleagues establish an initial pipeline in C. elegans to screen autism-associated missense mutations for functional effects.

Paul Sternberg and colleagues establish an initial pipeline in C. elegans to screen autism-associated missense mutations for functional effects.

Susan Bookheimer and colleagues show that the degree of sensory overresponsivity in individuals with autism may be driven by distinct patterns of connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and amygdala.
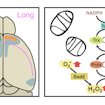
Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, Thomas Maynard and colleagues show that a mouse model of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome has fewer long-distance cortico-cortical connections, which is caused in part by mitochondrial dysfunction.
Two studies from Brigitta Monz, Richard Houghton and colleagues provide examples of the effectiveness of SPARK’s research match program to rapidly recruit thousands of individuals for the large-scale testing of research questions.
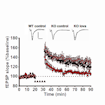
Peter Kind and colleagues show that brief treatment with lovastatin results in sustained correction of physiological and behavioral deficits in a rat model of fragile X syndrome.
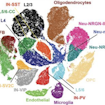
Using single-nucleus RNA sequencing of postmortem cortical tissue from individuals with ASD, Arnold Kriegstein and colleagues identify upper-layer excitatory neurons and microglia as key cell types affected in ASD.
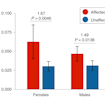
Timothy Yu and colleagues analyzed exome sequencing data to estimate that recessive mutations contribute to approximately 5 percent of all cases of autism, including 10 percent of females.
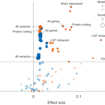
Olga Troyanskaya, Robert Darnell and colleagues applied deep-learning methods to whole-genome sequencing data from SSC families and identified a clear enrichment for de novo noncoding variation in ASD.
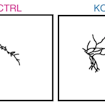
James Ellis and colleagues used a sparse co-culture system for iPSC-derived cortical neurons to assess neuronal connectivity, demonstrating increased connectivity in SHANK2-mediated ASD.

Mark Zylka and colleagues generated single-cell RNA-seq data from wild-type mouse cortex during early development and demonstrated how such a resource can be used to identify putative brain disorder subtypes based on expression profiles.